Artificial intelligence (AI) has come a long way from being a futuristic concept to a disruptive force that powers today’s business transformation. As AI adoption grows, it becomes increasingly important to understand its different classifications—particularly the distinction between Horizontal AI and Vertical AI.
In the world of AI, the discussion often revolves around specific industry use cases, leading many to focus on Vertical AI. However, Horizontal AI is equally, if not more, impactful, given its broad applicability across various industries. This blog dives deep into what Horizontal AI is, how it differs from Vertical AI, and why businesses need to embrace Horizontal AI for future-proof scalability and innovation.
Understanding Horizontal AI
Horizontal AI refers to AI models, platforms, and applications designed to serve a broad range of industries and functions. Unlike industry-specific solutions, Horizontal AI operates across sectors, providing flexible and reusable tools that can be applied to different contexts without significant re-engineering.
For example, Natural Language Processing (NLP) is a horizontal AI technology that can be utilized in customer service (e.g., chatbots), healthcare (e.g., patient data analysis), finance (e.g., fraud detection), and many other sectors. Computer vision is another Horizontal AI tool that finds use in security, manufacturing, retail and more
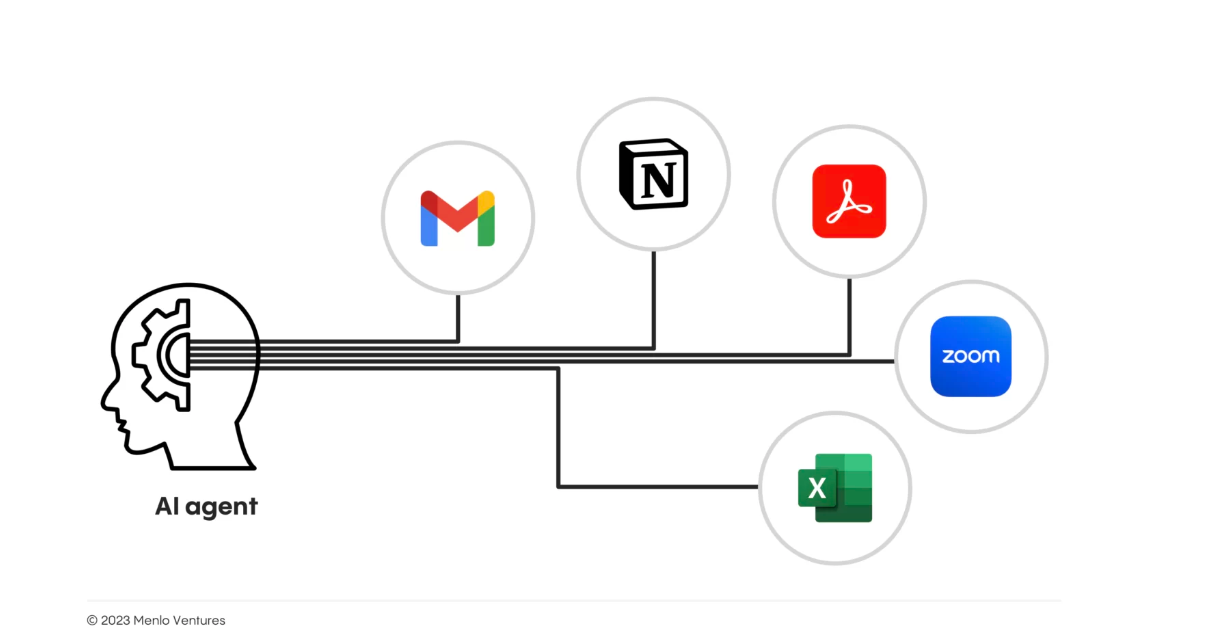
Source: Menlo Ventures Report
It’s not difficult to envision a future where AI has access to every spoken word and mouse click—and we welcome it. AI has the potential to significantly boost productivity if it’s granted access to an entire corpus of work, including calls, meetings, emails, notes, and even browser searches. While today we wrestle with the balance between privacy and productivity, this trade-off will become more acceptable as AI continues to gain our trust.
Legislation and corporate policies will need to evolve, but with the right governance, role-based access control (RBAC), and secure access to an enterprise’s knowledge repository (including emails, documents, and presentations), AI will become an invaluable tool for automation and collaboration, functioning as an extension of the human team.
As AI continues to evolve, these tools will become essential in helping us work faster, think smarter, and excel in our roles. The novelty of AI will fade, and it will become a natural, expected collaborator throughout the workday.
Potential targets of horizontal use cases are well-established automation centers, offer a substantial volume of training data (e.g., knowledge base, support chat logs), and are the focus of cost optimization and productivity improvement efforts. For example, creative marketing tasks like writing advertising copy, blogs, or social media captioning can take hours or days for humans to author. In contrast, Generative AI can complete workable drafts in minutes, requiring only editing from humans. These efficiencies may even redefine job expectations, making prompt engineering (i.e., asking AI the right questions) a differentiating skill set. Ultimately, horizontal use cases will create a commercial foundation for more specialized applications. Enterprises must start deploying these early to help build capabilities and a knowledge base, making the value case for vertical applications over time. Its seen research teams summarize third-party information, product managers write requirements documentation, social media marketers refine copy, and customer service teams create case summaries and suggested resolutions. However, tangible ROI could depend on proprietary and serviceable data, secure model partitioning, talented product leaders and ML engineers, enabling MLOps tooling, and new commercial and operating models. These are investments that enterprises should evaluate, whether they see themselves as early adopters, fast followers, or late entrants.
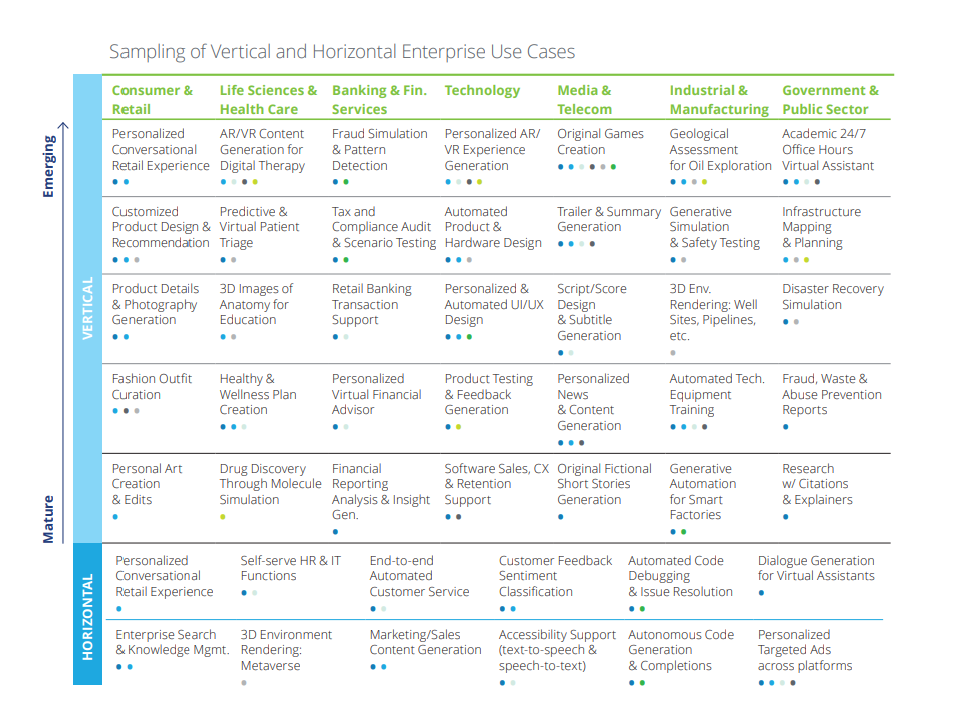
Source:Deloitte Report
Key Benefits of Horizontal AI
The broad applicability of Horizontal AI delivers several key advantages for businesses across industries:
1. Scalability and Efficiency
Horizontal AI allows businesses to implement a single AI solution across different departments or sectors. This offers unmatched scalability. Instead of building multiple niche-specific AI solutions, companies can deploy horizontal AI models that require only minimal tweaking to suit the needs of different functions.
“Gartner Says More Than 80% of Enterprises Will Have Used Generative AI APIs or Deployed Generative AI-Enabled Applications by 2026” – a significant portion of which will be powered by horizontal AI models. These models allow companies to scale AI efforts without the excessive costs of vertical-specific development.
2. Cost-Effectiveness
Building and maintaining specialized AI models for different industries can be costly. Horizontal AI eliminates the need for such redundancies by offering a solution that can adapt across industries. This reduces the time, effort, and financial resources spent on developing new AI solutions from scratch.
McKinsey study showed that businesses adopting AI solutions could see a reduction in costs by up to 20-30%, with horizontal AI playing a key role due to its reuse across multiple domains. Cost savings from deploying AI in a versatile manner gives businesses a competitive edge in a fast-changing technological landscape.
3. Versatility Across Use Cases
Horizontal AI models are flexible and can solve problems in various contexts, making them particularly useful for enterprises with diverse operations. A horizontal AI platform can be integrated into customer support for chatbots, data analysis for business intelligence, and predictive analytics for forecasting in multiple sectors.
In practice, tools like machine learning algorithms and computer vision find use in verticals as varied as healthcare, retail, manufacturing, and banking. Companies leveraging horizontal AI can move swiftly from one use case to another without requiring significant changes to the underlying AI model.
4. Democratization of AI
One of the most significant benefits of Horizontal AI is its ability to democratize access to AI technology. Startups, small businesses, and companies in non-tech industries often lack the deep expertise required to develop vertical-specific AI solutions. Horizontal AI provides these businesses with access to powerful, pre-built AI models that can be tailored to their unique needs.
5. Seamless Integration with Existing Systems
Another important advantage of Horizontal AI is that it integrates seamlessly with a variety of existing business systems. AI technologies like NLP, predictive analytics, and computer vision are designed to plug into existing tech stacks, regardless of the industry.
This integration helps businesses extract insights without needing to overhaul existing infrastructure. This approach stands in contrast to many vertical AI solutions, which often require significant customization and compatibility considerations.
Understanding Vertical AI
In contrast to Horizontal AI, Vertical AI is highly specialized and designed to address the unique challenges of a particular industry. Vertical AI solutions are built to provide deep expertise and precision within a niche. For example, AI in healthcare might focus on medical imaging, disease diagnosis, or drug discovery, while AI in finance might center around risk management, fraud detection, and portfolio management.
Although vertical AI excels in highly specialized use cases, its narrow focus can limit its scalability and applicability to other sectors.
Key Differences Between Horizontal AI and Vertical AI
| Factors | Horizontal AI | Vertical AI |
| Industry Focus | Industry-agnostic; applicable across different sectors with minimal modifications. | Industry-specific; tailored to address challenges unique to a particular domain. |
| Flexibility | Flexible and adaptable; can be implemented across multiple sectors without building new models. | Rigid; requires customization for the intricacies of the industry it serves. |
| Cost and Resources | More cost-effective; tools and models can be reused across industries. | More expensive to develop and maintain due to the need for specialized models for each application. |
| Time to Market | Shorter time to market; can be deployed rapidly across various sectors. | Longer development time; requires deep customization for each industry. |
| Innovation Potential | Fosters broad innovation; enables cross-industry experimentation and breakthroughs. | Focused innovation; limited to breakthroughs within the specific vertical it targets. |
Statistics: Horizontal AI Adoption on the Rise
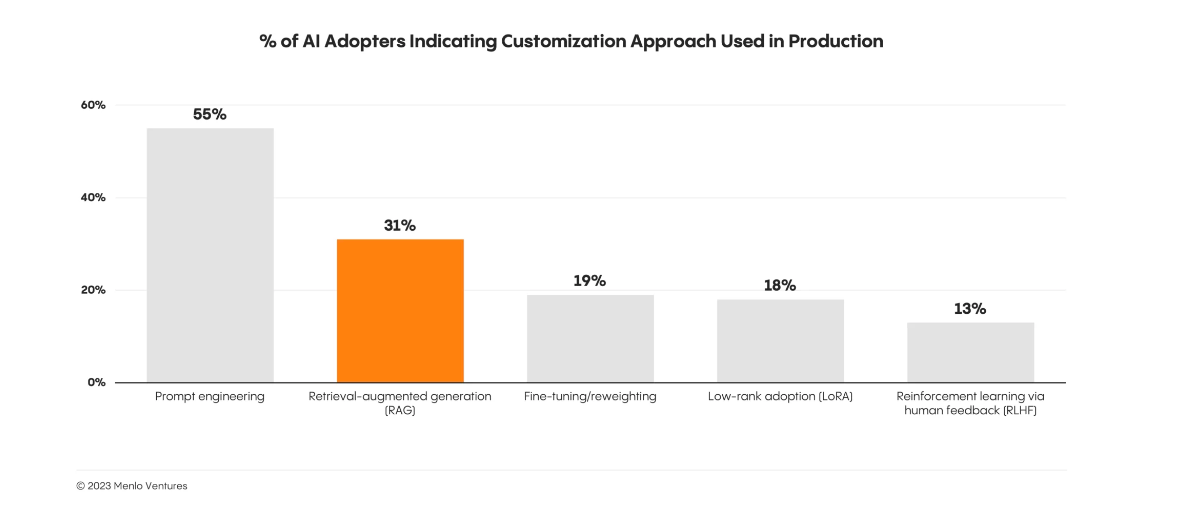
Source: Menlo Ventures Report
Horizontal AI thrives by leveraging customization techniques like Prompt Engineering and Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)—used by 55% and 31% of AI adopters, respectively—as these approaches allow AI systems to serve a wide range of tasks and functions across various sectors. Unlike Vertical AI, which is tailored to specific, narrow domains, Horizontal AI benefits from broader, scalable approaches like these, making it applicable across different business environments. The growing use of such techniques showcases how Horizontal AI can be fine-tuned for diverse industry applications while maintaining flexibility and reducing the need for highly specialized models.
Conclusion: Why Horizontal AI is the Future
Horizontal AI is poised to shape the future of artificial intelligence, offering broad applicability, cost-efficiency, and cross-industry innovation. While Vertical AI will continue to serve specific niches, businesses aiming to scale their AI capabilities across multiple sectors will find Horizontal AI indispensable.
In an age where digital transformation has become a necessity, can companies afford to limit themselves to siloed solutions? By embracing AI that transcends industries, they stand to unlock unprecedented efficiency and innovation—will your organization be ready to lead in the AI-powered future?