Digital transformation has been the mantra of corporate India for over a decade. Today, generative AI – machine learning models that create text, images, code and more – is emerging as the core engine of the next transformation wave. Leading analysts compare GenAI’s impact to that of electricity or the internet; McKinsey notes that AI “has arrived in the workplace and has the potential to be as transformative as the steam engine” of the Industrial Revolution. In India specifically, policymakers have tied the nation’s Vision 2047 ($30 trillion economy) to AI leadership, noting that future growth will be “powered by artificial intelligence”. In short, Indian companies that do not embrace generative AI risk being left behind.
Yet becoming an AI-first enterprise – one that embeds AI across business models and operations – is not a simple plug-and-play task. Success requires clear strategic intent, investment, and patience. Deloitte reports that most GenAI projects today are small pilots (typically <20 use cases), and only a minority of those pilots scale quickly.
Generative AI as the Foundation of Transformation
Generative AI differs fundamentally from traditional analytics. Instead of only analyzing or classifying data, generative models produce new content – drafting text, writing code, designing images, and more. The technology itself is evolving at breakneck speed. Foundation models (large pre-trained neural nets) such as OpenAI’s GPT-4 or Google’s PaLM 2 can understand and generate rich content across modalities. Enterprises that seize these advances can multiply their innovation rate. But Gartner cautions that these models are not magic: outputs can be inaccurate or biased, so human review is essential. Moreover, achieving true scale requires integration with core systems and data, not just point solutions.
Value and ROI of Generative AI
Investing in generative AI is only justifiable if the results are concrete. The good news for executives is that early cases are already delivering value. Only through this exploratory phase substantial returns on investment can be realized.

Source: pwc
Deloittle’s 2024 GenAI survey reports that almost all organizations see measurable ROI from their most mature GenAI projects. About 20% of those ventures have yielded extremely high returns (over 30% ROI), and 74% of leaders say their top GenAI initiative is meeting or beating expectations (Source).
Transforming Industries: Generative AI Use Cases for Indian Enterprises
Generative AI’s reach is broad. The following highlights illustrate how GenAI is reshaping key industries, with a focus on Indian context:
- Manufacturing and Industry 4.0: Indian manufacturers are beginning to apply GenAI for predictive maintenance and quality control. By analyzing sensor data and historical reports, GenAI can predict machine failures before they occur, schedule maintenance proactively, and simulate production line changes for optimal throughput.
- Retail and E-commerce: GenAI is revolutionizing how Indian retailers understand and engage shoppers. Large e-tailers like Myntra (fashion), Zomato and Swiggy (food delivery), and Brick-and-mortar chains use AI to personalize product recommendations and pricing in real time. It also powers dynamic pricing models – adjusting offers based on demand patterns and inventory levels.
- Healthcare and Pharma: India’s healthcare sector is rapidly adopting GenAI to improve diagnostics, research, and patient care. AI models can review medical images and patient records to flag anomalies. Generative AI assists medical professionals by summarizing case histories and clinical literature, enabling faster diagnosis.
- Telecom and IT Services: India’s massive IT and telecom sectors are naturally integrating GenAI into their offerings. Service teams use AI assistants (like GitHub Copilot) to auto-generate code, accelerating software development. As one McKinsey survey found, the technology sector leads in applying GenAI across more use cases than any other industry.
- Public Sector and Government: Even government services are seeing GenAI pilots. State and central agencies in India are developing AI chatbots to improve citizen interactions – for example, “Jugalbandi” is a GenAI-powered WhatsApp bot used by the Haryana government to handle tasks like pension payments and scholarship applications. Indian regulators are also studying how to use AI for tax and benefit fraud detection.
The Adoption Maturity Curve: From Pilots to AI Platforms
Deloitte’s GenAI tracking reports confirm this trend: nearly two-thirds of firms are running 20 or fewer experiments/POCs, and over 70% expect that less than one-third of those pilots will be fully scaled in the next 3–6 months. However, the pipeline is being built. Among the experiments that do scale, certain functions tend to lead. Deloitte reports that advanced GenAI initiatives often start in IT operations and core digital functions (about 28% of such projects), followed by back-office operations, marketing, and customer service.Gartner predicts that in coming years enterprises will treat GenAI like any other IT platform – with APIs, governance layers, and dedicated support teams.
Overcoming Barriers: Data, Governance, Talent, and Ethics
The path to AI-first is fraught with challenges. Executives frequently cite four broad areas of concern: data readiness, governance, workforce skills, and ethical/regulatory risks. Addressing these is as crucial as the technology itself.
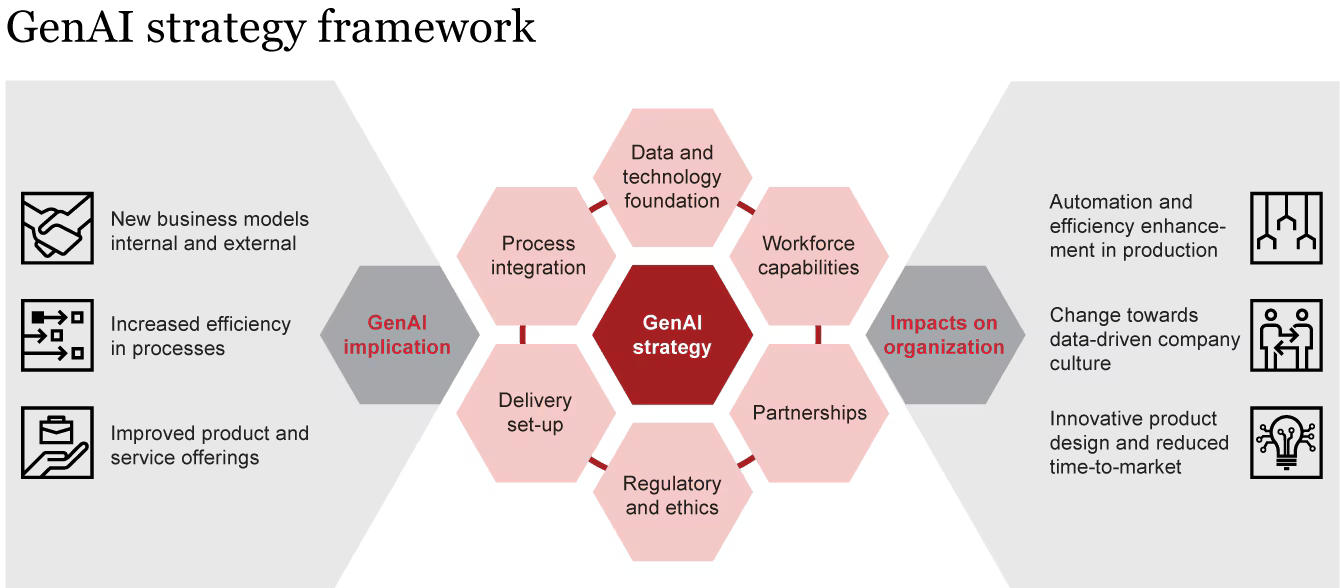
Source: pwc
- Data and Infrastructure: Generative AI systems are data-hungry and compute-intensive.In the near term, companies can partner with cloud providers (AWS, Azure, Google) which are rapidly expanding Indian data centers, to meet these demands.
- Governance and Regulatory: Generative AI brings new compliance questions. In practice, enterprises must build internal governance frameworks now. That means policies on acceptable AI use, regular model auditing, and oversight committees.
- Workforce and Skills: A strategic imperative is building human capital. Generative AI will not replace people wholesale, but it will shift skill requirements dramatically.
- Ethical and Cultural Challenges: Beyond formal governance, there is a human dimension. Many executives report fear or uncertainty about GenAI among their teams.
Strategic Roadmap: Becoming an AI-First Enterprise in India
Given these opportunities and hurdles, how should Indian business leaders proceed? Below are strategic guidance and action points to chart the AI-first journey:
- Elevate GenAI to the C-Suite Agenda: Leadership commitment is non-negotiable. BCG’s study emphasizes that true GenAI adoption requires visible CEO sponsorship – not just reliance on the CTO. In practice, this means establishing metrics and KPIs for GenAI initiatives (e.g. percentage increase in sales from AI-led campaigns, or reduction in call-center resolution time).
- Prioritize High-Impact Use Cases: Rather than scattering resources, focus on 20–30 critical use cases with clear business value.
- Invest in Data and Technology Foundations: Ensure that the company’s data architecture can support GenAI. This often means building or modernizing data lakes and warehouses so that all structured and unstructured data is accessible.
- Build Skills and Culture: As noted, the talent gap must be addressed. Initiate company-wide skilling programs – for example, short courses on prompt engineering, LLMs, and AI ethics.
- Govern and Ethically Manage AI: Establish clear AI governance from day one. Form a cross-functional ethics and compliance committee that reviews each GenAI deployment.
- Measure, Iterate and Scale: Maintain a disciplined project management approach. For every GenAI pilot, track the defined KPIs and measure actual ROI.
- Leverage Partnerships: No enterprise needs to go it alone. About half of companies in Asia plan to partner with external experts to advance GenAI (Source).
Organizations that move decisively to become “AI-first” will unlock new revenue streams,
operate more efficiently, and be better positioned in India’s rapidly digitalizing economy.
Conclusion
Generative AI represents a strategic inflection point for enterprises worldwide – and nowhere is this more true than in India’s dynamic market. For Indian C-suite executives and tech leaders, the mandate is clear: make generative AI a cornerstone of your digital strategy. Use it to reimagine customer experiences, products, and operations. Back this with data-driven planning, robust governance, and a long-term perspective. Organizations that move first will set the standard, capturing market share and talent, while shaping industries around AI-powered models.
In India’s ambitious quest to be a global technology leader, every industry – from manufacturing floors to boardrooms – will need to adopt an AI-first mindset.