Generative AI is rapidly becoming a business-critical technology worldwide. Leading analysts forecast trillions of dollars in value. For example, Goldman Sachs estimates GenAI could boost annual productivity by 1.5% – roughly $7 trillion over the next decade and McKinsey projects up to $7.9 trillion added to the global economy by leveraging generative models. IDC reports companies receive on average $3.70 of value for every $1 invested in GenAI (with top adopters realizing ~$10.30 per $1). These figures underscore why enterprises are moving GenAI from experimentation into core strategy. Businesses should therefore treat GenAI as a powerful force multiplier: automating routine work, personalizing services, and unlocking new insights. In short, GenAI is shifting from “exploratory pilots” to scaled deployments that drive efficiency and growth.
Quantifying ROI and Productivity Gains
Clear ROI metrics: Generative AI is already delivering measurable returns. IDC’s research (sponsored by Microsoft) finds that on average companies using GenAI see 3.7× ROI – i.e. $3.70 earned back per $1 spent – and the leading adopters see roughly $10.30 per $1. McKinsey observes that by late 2024 about 70% of businesses in finance, and similar shares in supply chain and marketing, had realized revenue uplifts from GenAI initiatives. These concrete gains help justify investment.
Economic impact and productivity: At the macro level, GenAI’s productivity potential is enormous. The World Economic Forum notes GenAI could add several percentage points to GDP growth; for example, a 1.5% boost equates to about $7 trillion worldwide. These figures translate into real business benefits. On the efficiency side, GenAI automates tasks so employees can focus on higher‑value work. Survey data and case studies confirm big time savings: for instance, 50% reductions in coding time have been reported when developers use AI coding assistants.
In India specifically, EY projects GenAI will boost productivity in financial services by 34–38% by 2030 (and up to 46% in banking operations).
Sector Impacts: Manufacturing, Healthcare, Retail, BFSI
Manufacturing:
GenAI is transforming product design and production. In R&D, generative design tools can optimize parts for weight and cost before any prototypes are built. On the shop floor, AI-driven predictive maintenance can cut downtime in half and reduce maintenance spend. Supply-chain and inventory planning benefit too: AI models can forecast demand and optimize logistics, reducing stockouts and excess inventory. Although exact ROI figures vary, survey data show manufacturers are prioritizing “high ROI investments” in AI. For example, Deloitte’s 2025 manufacturing outlook highlights that companies are focusing GenAI deployments on targeted use cases with clear value.
Healthcare:
Hospitals, insurers, and pharma companies are investing in GenAI to improve care and efficiency. McKinsey finds 85% of large US healthcare organizations are exploring or have adopted GenAI.
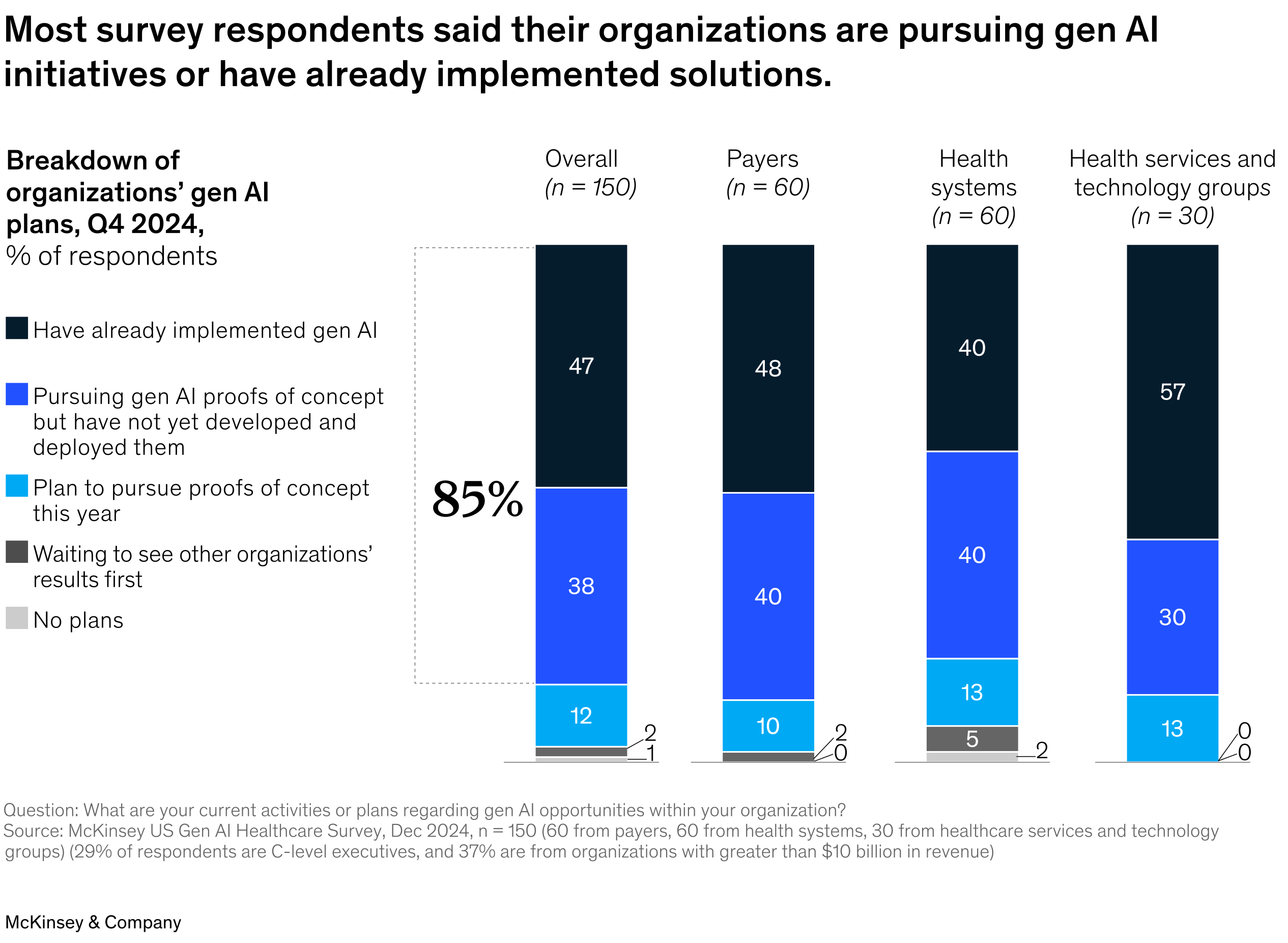
Source:Mckinsey
Typical use cases include automating administrative tasks (patient triage, billing), summarizing clinical notes, and even assisting in diagnostics (interpreting images or suggesting treatment options). Surveyed healthcare executives say the biggest opportunities are in administrative efficiency and clinical productivity. Even small efficiency wins here (e.g. 5–10% reduction in administrative costs) can translate into tens of millions saved in large health systems.
Retail and Consumer Goods:
Retailers deploy GenAI for customer experience and operations. Chatbots can guide shoppers, AI tools generate personalized marketing content, and recommendation engines optimize inventory. McKinsey projects GenAI could deliver $240–390 billion in value to the global retail sector, by boosting sales (through personalization) and cutting costs (through automation). In India, EY’s research shows the retail industry is bullish: 6% have already implemented GenAI, and 71% plan to adopt it within 12 months.

Source: EY
GenAI-powered tools could elevate retail profits by 20% by 2025. Use cases include dynamic pricing, virtual shopping assistants, and automated design of marketing campaigns.
Banking, Financial Services & Insurance (BFSI):
Financial firms are among the fastest GenAI adopters. They use AI chatbots and virtual assistants to handle customer inquiries, automate loan processing, and support underwriters. IDC notes the BFSI sector achieves the highest GenAI ROI among industries. In India, EY reports 74% of financial organizations have already launched GenAI proof-of-concept, and 42% are actively budgeting for AI.

Source:EY
Leading use cases include fraud detection (AI finds transaction anomalies), compliance monitoring, and personalized product recommendations. As a result, Indian banks expect large efficiency gains: EY predicts up to 46% productivity lift in banking operations by 2030 thanks to GenAI.
Scaling, Risks, and Conditions for Success
Achieving sustainable returns from GenAI requires overcoming key challenges. Many organizations struggle to move past pilots: Deloitte reports 70% of companies say fewer than one-third of their GenAI experiments reach production. Common hurdles include:
- Data and Infrastructure: GenAI demands large amounts of quality data and significant compute power. Enterprises must invest in data pipelines, cloud or on-prem AI infrastructure, and possibly specialized hardware. Without a solid data foundation, models cannot deliver reliable results.
- Talent and Skills: The top barrier is a skills gap. IDC highlights that lack of AI expertise (both technical and business) is the greatest hurdle. Nearly 30% of firms report lacking internal AI skills. Organizations must train or hire data scientists, AI engineers, and business leads who can steer GenAI projects. Partnerships with experienced vendors and hyperscalers can help bridge this gap.
- Governance and Risk: Especially in regulated industries, concerns about data privacy, security, and model bias are real. For example, banks must ensure GenAI tools comply with data localization and confidentiality rules.
- Change Management: Deploying GenAI often requires reconfiguring business processes and getting buy-in across functions. Gartner recommends combining quick wins (to build momentum) with strategic initiatives aligned to business goals.
Despite these challenges, the long-term outlook is positive. Many leaders acknowledge it may take 12+ months to fully realize GenAI’s value, and they are prepared to wait – Deloitte finds 76% would give AI initiatives a year or more before pulling back. The key is a disciplined approach: start with use cases that promise clear ROI, measure outcomes rigorously, and scale incrementally.
Conclusion
Generative AI is no longer just a technology trend – it’s a strategic imperative for enterprises. Its ability to slash costs, boost output, and open new growth avenues has been validated by global research firms. From $4.4 trillion in productivity potential to multi-billion-dollar impacts in key sectors, the data are clear: GenAI can pay off (Source). Forward-looking companies in banking, manufacturing, healthcare, retail and beyond are already seeing these gains. To capture the full benefit, however, firms must approach GenAI strategically – investing in talent and infrastructure, managing risks, and measuring real outcomes. In this way, generative AI will become a sustainable source of competitive advantage. As one expert notes, GenAI “has moved from the experimental to the essential”. For business leaders today, that means integrating AI solutions that solve end-to-end challenges, and scaling them to drive lasting ROI.